Winners / Selection Rationale
Oisix Inc.
2008 8th Porter Prize Winner Online grocery store
On-line retailer specializing in safe food
Industry Background
Although Japan's natural food market has grown rapidly in recent years (from $13.5 billion in 1999 to an estimated $24 billion in 2008), it is still very small compared with the US and Europe. The organic food market, at $2.6 billion, accounted for one tenth of the health food market in Japan, compared with $17 billion in the US and $18 billion in Europe. Increasing growth is expected in this market as concern over food safety grows.
Executive Summary
Oisix started its business in June 2000. At that time, homemakers did not usually order vegetables online, nor did many farmers sell their produce directly to small independent retailers.
Oisix specializes in online sales of organic and natural food based on the concept of promoting "food that producers would feel good about feeding to their own children." Offering 2,300 items, it is the largest web-based food retailer and the fastest growing one among the top three natural food retailers. Sales have grown at 35% annually since the company reached profitability in 2002. Both number of customers and sales per customer have grown, with 30,000 members in the Oisix Club regular purchase program spending on average 12,750 yen per month (2008). Sales of its closest competitor are one tenth of Oisix's sales. The other two sell through catalogs, and they do not sell online.
Oisix specializes in online sales of organic and natural food based on the concept of promoting "food that producers would feel good about feeding to their own children." Offering 2,300 items, it is the largest web-based food retailer and the fastest growing one among the top three natural food retailers. Sales have grown at 35% annually since the company reached profitability in 2002. Both number of customers and sales per customer have grown, with 30,000 members in the Oisix Club regular purchase program spending on average 12,750 yen per month (2008). Sales of its closest competitor are one tenth of Oisix's sales. The other two sell through catalogs, and they do not sell online.
Unique Value Proposition
Oisix's target customers are people who care about food safety and taste. Its target segment is broader than the niche segment of organic food enthusiasts.
Oisix's product assortment is as follows: 1)perishable food items (fruit, vegetables, meat, and seafood), 2) nonperishable food items (frozen foods, prepared foods, liquor, canned & dry goods, teas & drinks, baby food, and pet food), and 3) food-related products (books about food and cooking, kitchen products, and bath products). Fruit and vegetables are the main products, comprising 30% of total sales.
All the products Oisix sells must meet its safety standards, which cover farm products, stock farm products, aquatic products, processed foods, liquor, pet food, and home and kitchen products. These standards have been posted on the company's website.
After safety, the next most critical element in the value offered is taste. Oisix emphasizes the flavor of fruits and vegetables over their size and appearance, and in particular the flavor when eaten not when harvested.
The third critical element of value offered is ease of shopping. Oisix charges no membership fees, and customers can order as even just one product. Deliveries are available seven days a week, with a choice of six different time slots. This is very different from catalogue-based organic food retailers, who charge membership fees, sell a variety of merchandise as a basic package, and offer additional options with a less flexible delivery schedule.
Oisix's prices are similar to the prices charged by organic food retailers selling through catalogues and those charged for organic food items sold in organic food stores.
Oisix's product assortment is as follows: 1)perishable food items (fruit, vegetables, meat, and seafood), 2) nonperishable food items (frozen foods, prepared foods, liquor, canned & dry goods, teas & drinks, baby food, and pet food), and 3) food-related products (books about food and cooking, kitchen products, and bath products). Fruit and vegetables are the main products, comprising 30% of total sales.
All the products Oisix sells must meet its safety standards, which cover farm products, stock farm products, aquatic products, processed foods, liquor, pet food, and home and kitchen products. These standards have been posted on the company's website.
After safety, the next most critical element in the value offered is taste. Oisix emphasizes the flavor of fruits and vegetables over their size and appearance, and in particular the flavor when eaten not when harvested.
The third critical element of value offered is ease of shopping. Oisix charges no membership fees, and customers can order as even just one product. Deliveries are available seven days a week, with a choice of six different time slots. This is very different from catalogue-based organic food retailers, who charge membership fees, sell a variety of merchandise as a basic package, and offer additional options with a less flexible delivery schedule.
Oisix's prices are similar to the prices charged by organic food retailers selling through catalogues and those charged for organic food items sold in organic food stores.
Value Chain
Technology development
Oisix's R&D efforts focus on improving web site usability and on packaging that prevents loss of flavor and freshness.
Most Oisix customers finish shopping in less than 15 minutes and purchase 14 items on average. Importance is given to enabling customers to find what they want quickly so that they can buy small amounts of many items in a short time. Customers can select certain products as a set (called "My Set,") and have these items automatically placed into the shopping cart each time they log onto the website for shopping. Oisix also makes recommendations based on each customer's shopping history.
Since Oisix relies on third party shippers for delivery of its products, it is difficult for the company to control the care with which products are handled during delivery. Thus Oisix has been improving its product packages to better protect perishable products. Examples include special boxes for tomatoes, special shock-absorbing egg cartons and film for preserving freshness. The delivery process is analyzed by such means as placing on shipping boxes devices that record temperature and impact.
Procurement
Oisix procures vegetables, fruits, etc. directly from producers. Oisix's procurement policy is "food that the producers would feel good about feeding to their own children." All the products Oisix sells must meet its quality and safety standards. Oisix regularly consults the cultivation control logs submitted by the producers to verify production methods. Food items other than vegetables and fruit have to be approved by the Audit Committee for Food Safety, which Oisix established. This committee, which meets once a month, comprises six members, including a nutritionist, cooking experts, and homemakers. It checks items such as whether additives are within approved limits, whether main ingredients are certified as non-GMO and whether acceptable animal feeds were used. For fruits and vegetables, cultivation control logs obtained from producers show growing methods and history of use of fertilizers and pesticides. Oisix only purchases products that have received less than half the pesticides and fertilizers of conventionally farmed products.
Oisix conveys to producers customer complaints and feedback in order to deepen the producers' understanding about what customers expect in "delicious" foods. Oisix motivates producers by giving a "Farmer of the Year" award to the top three farmers, selected from among the 1,000 farmers who sell their produce through Oisix. Some 200 farmers attended the award ceremony in 2008.
Inbound logistics
Oisix places orders with producers only after receiving customers' orders. This result in lower inventory costs and an inventory disposal rate of less than 1%.
Operation
Oisix takes orders online only, which allows it to swiftly respond to fluctuations in production volume, which is one of the major challenges of selling organic food. When Oisix can buy popular products in large quantities, it displays this item prominently on its website to encourage sales and reduce inventory. When a large harvest of an item is anticipated, Oisix places it prominently on the web site to promote demand. When orders reach the expected harvest amount, the order management system displays "sold out" for that item.
Outbound logistics
Oisix delivers its products to the customers using third-party next-day delivery services. As a result, customers can select the delivery date and choose from six time slots per day.
Sales and marketing
Oisix does not spend much to acquire new customers. It places advertisements in blogs on the Internet, by paying a contingency fee, and posts advertisements on the websites of catalog retailers. It also increases its exposure by selling its products at Natural Lawson, a convenience store chain that specializes in natural products.
Oisix communicates detailed information for each perishable item, and also for prepared food items. It states the place of production, provides the name and a photograph of the producer, indicates the method of cultivation, and gives nutritional information, as well as cooking instructions.
After-sales service
Since order management is automated, Oisix can operate with a small support organization. Instead, the company focuses its sales support on advice about how to prepare its products for maximum enjoyment. For example, it sends occasional e-mails about products purchased including seasonal suggestions. First-time Oisix purchasers receive a message from the producer on the evening of the delivery day.
Human resource management
Oisix conducts the following activities in order to develop better understanding of products and producers:
1) Once every quarter employees of Oisix, including those who work for the IT and accounting divisions, visit producers and cook the food items being provided. For example over 100 people including 76 employees and some family members participated in such an event in April 2008. 2) Four or five times a year all Oisix employees spend one hour interviewing customers face to face. 3) In June 2008, Oisix started providing employees with a ¥10,000 stipend when they took paid-leave of longer than two consecutive days, to encourage them to enjoy eating good food.
Oisix's R&D efforts focus on improving web site usability and on packaging that prevents loss of flavor and freshness.
Most Oisix customers finish shopping in less than 15 minutes and purchase 14 items on average. Importance is given to enabling customers to find what they want quickly so that they can buy small amounts of many items in a short time. Customers can select certain products as a set (called "My Set,") and have these items automatically placed into the shopping cart each time they log onto the website for shopping. Oisix also makes recommendations based on each customer's shopping history.
Since Oisix relies on third party shippers for delivery of its products, it is difficult for the company to control the care with which products are handled during delivery. Thus Oisix has been improving its product packages to better protect perishable products. Examples include special boxes for tomatoes, special shock-absorbing egg cartons and film for preserving freshness. The delivery process is analyzed by such means as placing on shipping boxes devices that record temperature and impact.
Procurement
Oisix procures vegetables, fruits, etc. directly from producers. Oisix's procurement policy is "food that the producers would feel good about feeding to their own children." All the products Oisix sells must meet its quality and safety standards. Oisix regularly consults the cultivation control logs submitted by the producers to verify production methods. Food items other than vegetables and fruit have to be approved by the Audit Committee for Food Safety, which Oisix established. This committee, which meets once a month, comprises six members, including a nutritionist, cooking experts, and homemakers. It checks items such as whether additives are within approved limits, whether main ingredients are certified as non-GMO and whether acceptable animal feeds were used. For fruits and vegetables, cultivation control logs obtained from producers show growing methods and history of use of fertilizers and pesticides. Oisix only purchases products that have received less than half the pesticides and fertilizers of conventionally farmed products.
Oisix conveys to producers customer complaints and feedback in order to deepen the producers' understanding about what customers expect in "delicious" foods. Oisix motivates producers by giving a "Farmer of the Year" award to the top three farmers, selected from among the 1,000 farmers who sell their produce through Oisix. Some 200 farmers attended the award ceremony in 2008.
Inbound logistics
Oisix places orders with producers only after receiving customers' orders. This result in lower inventory costs and an inventory disposal rate of less than 1%.
Operation
Oisix takes orders online only, which allows it to swiftly respond to fluctuations in production volume, which is one of the major challenges of selling organic food. When Oisix can buy popular products in large quantities, it displays this item prominently on its website to encourage sales and reduce inventory. When a large harvest of an item is anticipated, Oisix places it prominently on the web site to promote demand. When orders reach the expected harvest amount, the order management system displays "sold out" for that item.
Outbound logistics
Oisix delivers its products to the customers using third-party next-day delivery services. As a result, customers can select the delivery date and choose from six time slots per day.
Sales and marketing
Oisix does not spend much to acquire new customers. It places advertisements in blogs on the Internet, by paying a contingency fee, and posts advertisements on the websites of catalog retailers. It also increases its exposure by selling its products at Natural Lawson, a convenience store chain that specializes in natural products.
Oisix communicates detailed information for each perishable item, and also for prepared food items. It states the place of production, provides the name and a photograph of the producer, indicates the method of cultivation, and gives nutritional information, as well as cooking instructions.
After-sales service
Since order management is automated, Oisix can operate with a small support organization. Instead, the company focuses its sales support on advice about how to prepare its products for maximum enjoyment. For example, it sends occasional e-mails about products purchased including seasonal suggestions. First-time Oisix purchasers receive a message from the producer on the evening of the delivery day.
Human resource management
Oisix conducts the following activities in order to develop better understanding of products and producers:
1) Once every quarter employees of Oisix, including those who work for the IT and accounting divisions, visit producers and cook the food items being provided. For example over 100 people including 76 employees and some family members participated in such an event in April 2008. 2) Four or five times a year all Oisix employees spend one hour interviewing customers face to face. 3) In June 2008, Oisix started providing employees with a ¥10,000 stipend when they took paid-leave of longer than two consecutive days, to encourage them to enjoy eating good food.
Fit among Activities
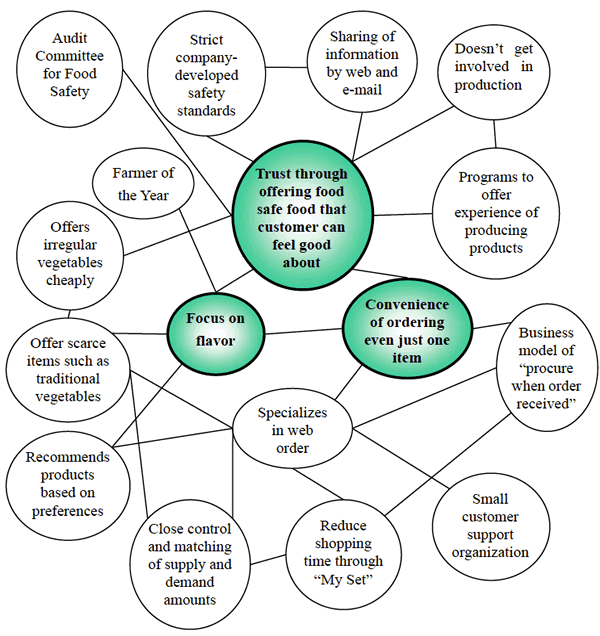
Oisix's activities are selected and combined to focus on achieving differentiation through the three factors of building trust through safe food that customers can feel good about, achieving top flavor and offering convenience.(See Oisix activity system map on next page.)
Innovations that Enabled Strategy
- Oisix aims to establish a new business that has no precedent in the US, the leading market for online businesses.
- Logistics model of harvesting fresh foods after order is received.
Consistency of Strategy Over Time
- The policy of selling only "food that the producers would feel good about feeding to their own children" and the Audit Committee for Food Safety have been implemented since founding of the company in 2000.
- Since founding, orders have only been taken on-line.
Trade-offs
- Does not take orders other than via the Internet.
- Does not sell food items in pre-determined sets.
- Does not sell vegetables produced by conventional methods and prepared foods with many additives.
- Does not sell products unrelated to food. For example, it does not sell diapers and tissue paper, which are popular among expecting mothers or mother who stay at home (and who would be happy to order these items online).
- Does not enter the wholesale business to pursue an increase in sales.
- Does not undertake actual food production.
Profitability
Both return on invested capital and return on sales exceed industry average.
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on invested capital = Operating income / Average invested capital
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on sales =Operating income / Net sales
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry averag over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | |
| 85.5%P | -121.3%P | 14.4%P | 19.4%P | 11.33.6%P | 406.9%P |
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry average over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | |
| 3.2%P | -2.9%P | 0.2%P | 1.3%P | 3.7%P | 2.1%P |
Activity System Map
Winners PDF
- 2008 Porter Prize Winners PDF (All of the award company in this year are published. )





