Winners / Selection Rationale
Suruga Bank Ltd.
2003 3rd Porter Prize Winner Regional bank
Continuous development of new products and unique services based on highly original approaches, which enabled for Suruga Bank to provide services that had not been available to its customers.
Unique Value Proposition
Suruga Bank is a regional bank headquartered in Numazu City in Shizuoka Prefecture. As a cornerstone of its specialization in the retail market, Suruga Bank provides unique products based on a highly original perspective, with the goal of responding to individual customer needs on a one-to-one basis, as expressed by its vision to be the best "concierge." For example, Suruga dispensed with the requirement of a minimum of two years' employment at the time of mortgage loan application submission, marking a departure from a common industry practice. This change enabled Suruga to extend loans to competent system engineers who tended to move from one place of employment to another. Furthermore, they were the first Japanese financial institution to develop and market a mortgage loan product that could be extended to individuals who had not been able to acquire a mortgage loan for having been rejected for group-guaranteed life insurance. Suruga has 26 types of mortgage loan products, offered in combination with four types of mortgage loan insurance. This extensive product lineup, which can be combined with mortgage loan insurance makes it possible for the bank to meet specific customer needs. (cf. Most Japanese banks offer only one to five mortgage loan products).
As seen from these examples, many of Suruga Bank's products cater to customers who were unable to qualify for the ordinary mortgage loans offered by banks. Suruga positions its unique products as "dream enablers," without which customers would likely not realize their dream of owning a home (or condominium). (More than 90% of Suruga's mortgage loan customers purchased a type of mortgage loan product that cannot be found at other financial institutions.)
Suruga Bank has a very quick loan screening process, averaging a turn-around time of under 48 hours, with a same-day response quite common. The norm in the industry for mortgage loan screening is 3 to 5 days. Not only does Suruga Bank respond quickly to loan applications and offer an extensive product lineup, it also provides individuals an efficient way to search for real estate property search, as well as functioning as an effective sales channel for real estate providers (agents, housing developers, and builders among others), who also serve as mortgage loan sales partners for Suruga Bank. It also diminishes the likelihood of cancellations due to mortgage loan unavailability once a decision to purchase has been made, thereby reducing inefficiencies.
Suruga Bank tries to be the best "concierge" to non-mortgage loan customers by addressing the specific needs each individual on a "one-to-one" basis. Every member of the customer service staff can easily access individual customer information, and retrieve from the database a customer's entire transaction history and his or her approved loan limit. Such information enables the bank to propose service options that meet specific needs their customers hadn't even known existed.
As seen from these examples, many of Suruga Bank's products cater to customers who were unable to qualify for the ordinary mortgage loans offered by banks. Suruga positions its unique products as "dream enablers," without which customers would likely not realize their dream of owning a home (or condominium). (More than 90% of Suruga's mortgage loan customers purchased a type of mortgage loan product that cannot be found at other financial institutions.)
Suruga Bank has a very quick loan screening process, averaging a turn-around time of under 48 hours, with a same-day response quite common. The norm in the industry for mortgage loan screening is 3 to 5 days. Not only does Suruga Bank respond quickly to loan applications and offer an extensive product lineup, it also provides individuals an efficient way to search for real estate property search, as well as functioning as an effective sales channel for real estate providers (agents, housing developers, and builders among others), who also serve as mortgage loan sales partners for Suruga Bank. It also diminishes the likelihood of cancellations due to mortgage loan unavailability once a decision to purchase has been made, thereby reducing inefficiencies.
Suruga Bank tries to be the best "concierge" to non-mortgage loan customers by addressing the specific needs each individual on a "one-to-one" basis. Every member of the customer service staff can easily access individual customer information, and retrieve from the database a customer's entire transaction history and his or her approved loan limit. Such information enables the bank to propose service options that meet specific needs their customers hadn't even known existed.
Unique Value Chain
Product development
The product development criteria of Suruga Bank are threefold: 1) A new product must allow for customization to meet the individual customer's needs; 2) It must provide access to a niche market; and 3) It must not currently be offered by other banks. Suruga's ability to develop unique products is supported by its vast accumulation of loan screening data regarding an individual's repayment capabilities, its extensive assessment know-how, an automatic lending examination system, and a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. In addition, Suruga constantly works to develop channels for collecting detailed information concerning the financial status of individual customers and their financial needs. Suruga Bank also frequently conducts market surveys by mailing out questionnaires to identify latent customer needs. At the same time, the bank encourages its employees to maintain close contact with customers through daily activities, so as to gain a clear understanding of customers' needs. Two examples of the new products cited above were developed in response to reports by employees concerning unmet customer needs, based on responses during interviews with people in the real estate channel.
Suruga Bank took this thinking one step further and undertook a clear delineation of responsibility. Front-line employees were made responsible for proposing ideas for new products and services. Meanwhile, the corporate planning staff was assigned the task of taking the proposals and turning them into actual, marketable products. All employees have access to the bank's intranet system, named "21st Century Explorers." The proposed new product ideas posted on this site are thus made accessible to the entire staff. When a proposal is input into the system, the corporate planning department and the other departments directly involved are required to respond and provide a feedback within 48 hours. The site "21st Century Explorers" is one of the most active sites on the bank's intranet system, and since its inception, the ideas posted on this site have led to the development of more than ten new products, and also more than ten innovations for existing products.
Marketing and sales
Suruga Bank's sales activities for its existing customers are based on proposals developed through the use of a loan pre-approval system and a CRM system. Suruga is able to provide products and services quickly, and at a low cost as a result of the installation of these two systems.
Product/service provision channels
The bank's "Housing Loan Centers" are branch offices that specialize in the provision of mortgage loans. These branches are opened in strategic locations where mortgage loan demand is high, such as Tachikawa, Shinjuku, Omiya and Kashiwa (all within commuting distance to Tokyo) and Kohoku New Town, (near Yokohama). These locations are far outside of Suruga's original base of operations, namely Shizuoka and Kanagawa prefectures. For the convenience of customers who live in areas in which Suruga does not have branches, the bank had created the most extensive ATM network in the industry by forming alliances with convenience store chains and the postal service network. Suruga also made on-line banking services a priority by opening and operating eight on-line branches, with each one specialized in a different niche segment.
Planning
Seeking to be the best "concierge" and a pioneer in the industry, Suruga Bank hosts an annual event called "The Junior Board," during which front-line employees develop various new plans and present them directly to the CEO. The management also introduced an important change in the corporate culture. Whereas previously emphasis had been placed on minimal tolerance for failures, the management now encourages employees to act quickly on ideas with a 65% or higher probability of success. Consequently, the time between an idea's proposal and its implementation has been reduced considerably.
Firm infrastructure
The back office operations of branch offices (which include form processing for bill issuing and foreign exchange, and the handling of telephone inquiries) have been centralized at the headquarters to improve the efficiency of branch operations. The remaining administrative tasks at branch offices are handled by the staff, and each staff member is expanding the number of tasks for which they are responsible. The aim is to perform five different duties as a professional..
Suruga Bank has developed a database of rules and procedures, enabling branch employees to access it and make quick on-line inquiries while seated at their desks dealing with a customer. This system, which facilitates inquiries and the retrieval not only of rules and regulations, but also work process flow charts, makes it much easier for inexperienced junior staff and part-time staff to follow the correct procedures.
The product development criteria of Suruga Bank are threefold: 1) A new product must allow for customization to meet the individual customer's needs; 2) It must provide access to a niche market; and 3) It must not currently be offered by other banks. Suruga's ability to develop unique products is supported by its vast accumulation of loan screening data regarding an individual's repayment capabilities, its extensive assessment know-how, an automatic lending examination system, and a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. In addition, Suruga constantly works to develop channels for collecting detailed information concerning the financial status of individual customers and their financial needs. Suruga Bank also frequently conducts market surveys by mailing out questionnaires to identify latent customer needs. At the same time, the bank encourages its employees to maintain close contact with customers through daily activities, so as to gain a clear understanding of customers' needs. Two examples of the new products cited above were developed in response to reports by employees concerning unmet customer needs, based on responses during interviews with people in the real estate channel.
Suruga Bank took this thinking one step further and undertook a clear delineation of responsibility. Front-line employees were made responsible for proposing ideas for new products and services. Meanwhile, the corporate planning staff was assigned the task of taking the proposals and turning them into actual, marketable products. All employees have access to the bank's intranet system, named "21st Century Explorers." The proposed new product ideas posted on this site are thus made accessible to the entire staff. When a proposal is input into the system, the corporate planning department and the other departments directly involved are required to respond and provide a feedback within 48 hours. The site "21st Century Explorers" is one of the most active sites on the bank's intranet system, and since its inception, the ideas posted on this site have led to the development of more than ten new products, and also more than ten innovations for existing products.
Marketing and sales
Suruga Bank's sales activities for its existing customers are based on proposals developed through the use of a loan pre-approval system and a CRM system. Suruga is able to provide products and services quickly, and at a low cost as a result of the installation of these two systems.
Product/service provision channels
The bank's "Housing Loan Centers" are branch offices that specialize in the provision of mortgage loans. These branches are opened in strategic locations where mortgage loan demand is high, such as Tachikawa, Shinjuku, Omiya and Kashiwa (all within commuting distance to Tokyo) and Kohoku New Town, (near Yokohama). These locations are far outside of Suruga's original base of operations, namely Shizuoka and Kanagawa prefectures. For the convenience of customers who live in areas in which Suruga does not have branches, the bank had created the most extensive ATM network in the industry by forming alliances with convenience store chains and the postal service network. Suruga also made on-line banking services a priority by opening and operating eight on-line branches, with each one specialized in a different niche segment.
Planning
Seeking to be the best "concierge" and a pioneer in the industry, Suruga Bank hosts an annual event called "The Junior Board," during which front-line employees develop various new plans and present them directly to the CEO. The management also introduced an important change in the corporate culture. Whereas previously emphasis had been placed on minimal tolerance for failures, the management now encourages employees to act quickly on ideas with a 65% or higher probability of success. Consequently, the time between an idea's proposal and its implementation has been reduced considerably.
Firm infrastructure
The back office operations of branch offices (which include form processing for bill issuing and foreign exchange, and the handling of telephone inquiries) have been centralized at the headquarters to improve the efficiency of branch operations. The remaining administrative tasks at branch offices are handled by the staff, and each staff member is expanding the number of tasks for which they are responsible. The aim is to perform five different duties as a professional..
Suruga Bank has developed a database of rules and procedures, enabling branch employees to access it and make quick on-line inquiries while seated at their desks dealing with a customer. This system, which facilitates inquiries and the retrieval not only of rules and regulations, but also work process flow charts, makes it much easier for inexperienced junior staff and part-time staff to follow the correct procedures.
Fit among Activities
One of the key activities of Suruga Bank is loan screening. The bank has accumulated a wealth of personal financial data over the years in the course of extending small-amount loans to individuals, as well as extensive loan screening know-how, which has enabled the development of an automatic lending examination system. This system, applied to both small loans and mortgage loans, is what has allowed Suruga Bank to dramatically speed up the loan screening process.
The distinctive feature of Suruga's screening process is the emphasis placed on an individual's loan repayment capabilities rather than on the collateral value of the mortgage. By measuring and assessing an individual's ability to repay the loan, Suruga has been able to develop new loan products from an innovative perspective.
Suruga also analyzes the financial requirements of existing customers, and by linking the CRM system and the preliminary loan screening process, the bank's loan officers can talk to customers with a clear idea of their credit lines, and can propose numerous options.
Other key activities at Suruga Bank include the sharing of the bank's vision of being the best "concierge," and motivating employees by encouraging them to propose new services and other improvements. These activities inspire and empower employees, who in turn develop new products and increase loan sales by making proposals to customers, while making best use of the loan screening data, the CRM information, and the market information gained through real-estate channels.
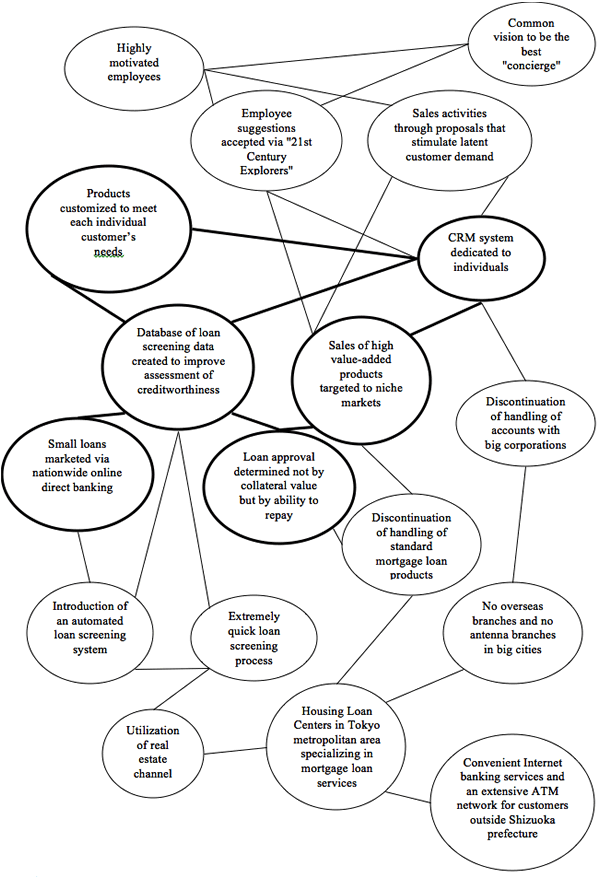
(Please refer to the attached "Activity System Map" for a more detailed account of the relationship between these activities.)
The distinctive feature of Suruga's screening process is the emphasis placed on an individual's loan repayment capabilities rather than on the collateral value of the mortgage. By measuring and assessing an individual's ability to repay the loan, Suruga has been able to develop new loan products from an innovative perspective.
Suruga also analyzes the financial requirements of existing customers, and by linking the CRM system and the preliminary loan screening process, the bank's loan officers can talk to customers with a clear idea of their credit lines, and can propose numerous options.
Other key activities at Suruga Bank include the sharing of the bank's vision of being the best "concierge," and motivating employees by encouraging them to propose new services and other improvements. These activities inspire and empower employees, who in turn develop new products and increase loan sales by making proposals to customers, while making best use of the loan screening data, the CRM information, and the market information gained through real-estate channels.
(Please refer to the attached "Activity System Map" for a more detailed account of the relationship between these activities.)
Innovations that Enabled Strategy
- The establishment of Housing Loan Centers (HLC) with specific key functions
- The opening of HLCs in the Tokyo metropolitan area, on-line banking functionality, and the creation of the industry's largest ATM network, all of which eliminated geographic and time constraints on sales activities
- The introduction of an automatic loan screening system, which enables extremely quick assessments, unique product development and sales through proposal-making, as well as reduces the likelihood of cancellations after purchase decisions have been made
- The installation of the Intranet system "21st Century Explorers", which enables the collection of new product ideas and proposals from front-line staff, and makes this data available to all staff members
- The establishment of the "Junior Board," whereby the front-line staff is given the opportunity to develop medium- to longer-term proposals and present them directly to the CEO
Consistency of Strategy Over Time
In 1988, when full banking services were a common practice of all banks, Suruga Bank made the strategic decision to specialize in retail banking services for individual customers, and has maintained this strategy ever since. At Suruga's loans to individuals comprise 63.8% of the total outstanding loan balance, which is the highest percentage of loans to individuals in the industry and far ahead of the second bank in this regard. (Note: Suruga Bank continues to conduct loan transactions with small-to-medium-size businesses through direct channels at its headquarters and one centralized corporate banking branch.)
Trade-offs
- By concentrating on retail banking for individuals, Suruga Bank chose to discontinue its transactions and services for big corporations. As a result, the bank's need for overseas branches was significantly diminished, and branches that had relied heavily on corporate banking and business processes for derivatives and M&A were dramatically reduced. After some transition years, the bank closed down all of these operations. Suruga also stopped making corporate sales calls, and no longer made visits to an individual customer's workplace.
- The creation of an extensive ATM network and on-line banking systems greatly reduced the importance of a network of domestic branches. Seeing this result, Suruga closed all branches other than those in its core market in Aichi and Yamanashi prefectures.
- With personnel and funds freed up by these developments, Suruga Bank opened HLCs in the Tokyo metropolitan area, providing work to employees. By specializing in individual customers, the bank was able to concentrate its resources on building excellent information systems.
- Suruga Bank does not actively market the type of standard mortgage loan packages that are offered by other banks, because it aims to provide unique products that are available only at Suruga Bank.
Profitability
In recent years, more and more banks, including mega-banks, have started to emphasize retail banking, which has brought about a price competition in the mortgage loan market. However, because of its unique products, Suruga Bank has been able to avoid a price competition, and as a result, it has secured a loan margin spread that is double the industry average. The bank's operating profit margin is much higher than the industry average, and its return on invested capital has also consistently exceeded the industry average.
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on invested capital = Operating income / Average invested capital
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on sales =Operating income / Net sales
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry averag over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | |
| 0.8%P | 0.7%P | 0.6%P | 0.4%P | 0.2%P | 0.8%P |
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry average over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | |
| 25.9%P | 14.0%P | 9.6%P | 5.2%P | 5.1%P | 21.7%P |
Activity System Map
Winners PDF
- 2003 Porter Prize Winners PDF (All of the award company in this year are published. )





