Winners / Selection Rationale
NIDEC Corporation Precision Small Motor Division
2006 6th Porter Prize Winner Manufacturing of motors
Specialization in brushless DC motors, and achieving an overwhelming share of the global market through innovations, flexibility in responding to customer needs in design and manufacturing, and active new customer development.
Industry Background
The small motor manufacturing industry consists namely of three categories of products: DC motors with brushes, brushless DC motors, and AC motors. Brushless DC motors offer many advantages over motors with brushes, offering finer control of the rotation speed, lower rotation noise, the elimination of electro-magnetic noise, less electric consumption, great durability, and therefore better suited to the design of smaller and thinner motors. However, the manufacture of a brushless motor requires the use of semiconductor devices, which makes the manufacturing process more complicated and raises its cost. Brushless motors are used as components in a broad range of products, including hard-disk drives (HDDs), optical disc drives, fans, office automation equipment, home appliances and automobiles. As the range of use broadens, the price of brushless DC motors continues to decline, and there has also been an acceleration in the pace at which brushless DC motors are replacing AC & DC motors.
Mabuchi Motor, the winner of the Porter Prize in 2001, specializes in DC motors with brushes, and is a leader of the segment holding a 60% share of the global market. Mabuchi's strategy is to pursue standardization as the core concept, which is in marked contrast to NIDEC's strategy of flexibly customizing products to meet customers' specifications. The Porter Prize Organizing Committee believes there can be more than one excellent strategy in the same industry, and that both Mabuchi's award-winning strategy and NIDEC's strategy being awarded at this time are both viable excellent strategies.
NIDEC's Precision Micro Motor Division specializes in manufacturing brushless DC motors, and it accounts for 51% of total corporate sales. Its primary market is for use as a component for HDDs. NIDEC holds a 75% share of the global market in this segment, and an especially high market share of 90% in the smaller HDD market for laptop PCs.
Mabuchi Motor, the winner of the Porter Prize in 2001, specializes in DC motors with brushes, and is a leader of the segment holding a 60% share of the global market. Mabuchi's strategy is to pursue standardization as the core concept, which is in marked contrast to NIDEC's strategy of flexibly customizing products to meet customers' specifications. The Porter Prize Organizing Committee believes there can be more than one excellent strategy in the same industry, and that both Mabuchi's award-winning strategy and NIDEC's strategy being awarded at this time are both viable excellent strategies.
NIDEC's Precision Micro Motor Division specializes in manufacturing brushless DC motors, and it accounts for 51% of total corporate sales. Its primary market is for use as a component for HDDs. NIDEC holds a 75% share of the global market in this segment, and an especially high market share of 90% in the smaller HDD market for laptop PCs.
Unique Value to Proposition
NIDEC's core strategy is to find ways for brushless DC motors to replace AC motors and DC motors with brushes. Following this core strategy, NIDEC offers unique value that derives from the product features of the brushless DC motor, which includes extremely quiet rotation noise, finely controllable rotation speed, low electric consumption, smallness, flatness, long durability, and an absence of electro-magnetic noise emissions.
Furthermore, NIDEC has advantages over other competitors that also supply brushless DC motors. NIDEC offers a broader product range, and can respond to customer needs better and more quickly, thanks to its development engineering capabilities and manufacturing technology, with shorter delivery times, competitive prices and a stable supply ensured by active investments that precede market expansion.
NIDEC also has a distinctive leading-edge technology, and holds an overwhelming share of the global market for thin brushless DC flat motors.
NIDEC's target customers, which use the motors or a broad variety of applications, include manufacturers of IT equipment such as HDDs, optical disk drives, and fans, as well as producers of OA equipment, home appliances, and automobiles. As NIDEC designs products tailor-made to customers' specifications, it can selectively choose customers who are likely to place orders for large volume production lots per model to gain economies of scale and consequent price competitiveness. NIDEC values both information advantages and large volume production gains that are available when holding the top share in the global market, and once an application for a specific use is developed, NIDEC includes all major players for that application as its target customers.
Furthermore, NIDEC has advantages over other competitors that also supply brushless DC motors. NIDEC offers a broader product range, and can respond to customer needs better and more quickly, thanks to its development engineering capabilities and manufacturing technology, with shorter delivery times, competitive prices and a stable supply ensured by active investments that precede market expansion.
NIDEC also has a distinctive leading-edge technology, and holds an overwhelming share of the global market for thin brushless DC flat motors.
NIDEC's target customers, which use the motors or a broad variety of applications, include manufacturers of IT equipment such as HDDs, optical disk drives, and fans, as well as producers of OA equipment, home appliances, and automobiles. As NIDEC designs products tailor-made to customers' specifications, it can selectively choose customers who are likely to place orders for large volume production lots per model to gain economies of scale and consequent price competitiveness. NIDEC values both information advantages and large volume production gains that are available when holding the top share in the global market, and once an application for a specific use is developed, NIDEC includes all major players for that application as its target customers.
Unique Value Chain
Technology development
NIDEC acquired key technologies such as precision molding, precision measuring and metal machining technologies through M&As, which made it possible to differentiate itself by gaining a technological lead. For example, NIDEC is the first company in the world to mass-produce fluid dynamic bearing (FDB) motors, which require state-of-the-art precision machining and precision measuring technologies. NIDEC selectively acquired companies from outside its industry that owned these technologies, so that it could own these technologies in-house to mass-produce and market such leading-edge products. Through these acquisitions, NIDEC also gained ability to engineer and design manufacturing facilities that can protect and prevent the divulgence of the key technologies.
Manufacturing
NIDEC develops and manufactures its own production facilities, and has "made in the market" as a policy. Following this policy, it makes products near its customers, which makes it easier to respond swiftly with flexibility to customer needs.
Sales
NIDEC does not confine itself to selling its products to existing customer industries, but rather seeks areas of usage where brushless DC motors could improve the performance of final products capitalizing on the features of the brushless motors. In search of new usages, NIDEC's sales staff develop and present proposals to prospective customers, and each sales staff member is expected to visit at least 100 companies each month. Thanks to their efforts, brushless DC motors are now used in products not thought to contain motors, such as electric rice cookers and "Washlet" toilet seats featuring a water-jet cleaner and blower.
Pricing cannot be determined by the Sales Division alone but is done through discussions and with the agreement of the Manufacturing Division. Within NIDEC, the Manufacturing Division is held responsible for profitability, and strongly resists discounting. Such an arrangement to prevents discounting by the Sales Division as an easy way of expanding the market share. Strategic pricing, which may be required sell for selling in a new area of application, can result in a short-term set back in profitability, and therefore requires a decision by top management.
The Sales Division is responsible for keeping agreed-upon delivery dates. In cases where the Manufacturing Division faces difficulties in meeting the delivery date schedule due to shortages of either materials or manpower, the Sales Division makes every effort to procure the necessary resources to expedite delivery.
Firm infrastructure
There is a deep-rooted corporate culture in NIDEC whereby employees are requested to step up and do whatever is needed regardless of their job descriptions, job titles or positions within the organization. The NIDEC motto is: "Do anything immediately without fail, until the task can be accomplished."
NIDEC emphasizes what it calls the "3Q and 6S Index." The 3Qs refers to its three goals of achieving quality workers, a quality company, and quality products (3Qs). The 6Ss stand for sorting, tidying, cleaning, cleanliness, courtesy and discipline in Japanese. If these six functions are duly fulfilled, NIDEC believes it can achieve the 3Qs. NIDEC has developed criteria to assess the level of achievement in the 3Qs and the 6Ss, and requests a member of top management to periodically inspect and assess the level of achievement for these functions within each unit of the organization.
NIDEC acquired key technologies such as precision molding, precision measuring and metal machining technologies through M&As, which made it possible to differentiate itself by gaining a technological lead. For example, NIDEC is the first company in the world to mass-produce fluid dynamic bearing (FDB) motors, which require state-of-the-art precision machining and precision measuring technologies. NIDEC selectively acquired companies from outside its industry that owned these technologies, so that it could own these technologies in-house to mass-produce and market such leading-edge products. Through these acquisitions, NIDEC also gained ability to engineer and design manufacturing facilities that can protect and prevent the divulgence of the key technologies.
Manufacturing
NIDEC develops and manufactures its own production facilities, and has "made in the market" as a policy. Following this policy, it makes products near its customers, which makes it easier to respond swiftly with flexibility to customer needs.
Sales
NIDEC does not confine itself to selling its products to existing customer industries, but rather seeks areas of usage where brushless DC motors could improve the performance of final products capitalizing on the features of the brushless motors. In search of new usages, NIDEC's sales staff develop and present proposals to prospective customers, and each sales staff member is expected to visit at least 100 companies each month. Thanks to their efforts, brushless DC motors are now used in products not thought to contain motors, such as electric rice cookers and "Washlet" toilet seats featuring a water-jet cleaner and blower.
Pricing cannot be determined by the Sales Division alone but is done through discussions and with the agreement of the Manufacturing Division. Within NIDEC, the Manufacturing Division is held responsible for profitability, and strongly resists discounting. Such an arrangement to prevents discounting by the Sales Division as an easy way of expanding the market share. Strategic pricing, which may be required sell for selling in a new area of application, can result in a short-term set back in profitability, and therefore requires a decision by top management.
The Sales Division is responsible for keeping agreed-upon delivery dates. In cases where the Manufacturing Division faces difficulties in meeting the delivery date schedule due to shortages of either materials or manpower, the Sales Division makes every effort to procure the necessary resources to expedite delivery.
Firm infrastructure
There is a deep-rooted corporate culture in NIDEC whereby employees are requested to step up and do whatever is needed regardless of their job descriptions, job titles or positions within the organization. The NIDEC motto is: "Do anything immediately without fail, until the task can be accomplished."
NIDEC emphasizes what it calls the "3Q and 6S Index." The 3Qs refers to its three goals of achieving quality workers, a quality company, and quality products (3Qs). The 6Ss stand for sorting, tidying, cleaning, cleanliness, courtesy and discipline in Japanese. If these six functions are duly fulfilled, NIDEC believes it can achieve the 3Qs. NIDEC has developed criteria to assess the level of achievement in the 3Qs and the 6Ss, and requests a member of top management to periodically inspect and assess the level of achievement for these functions within each unit of the organization.
Fit among Activities
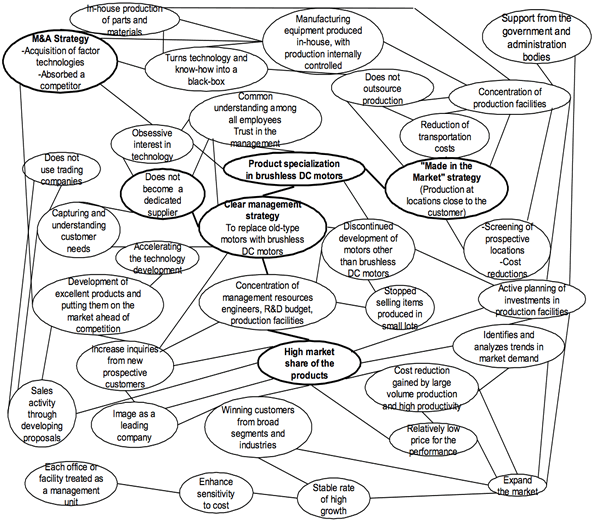
NIDEC's activities are selected and harmonized to achieve its key priorities of expanding market share and securing profits. To achieve these goals, NIDEC must best respond to customer needs with high technology, and at the same time, achieve efficiency in operations. More specifically, it constantly tries to improve its own technology so that customer needs may be fully met, and carries out M&As as needed to acquire the technologies necessary for enhancing both product technology and production technology. As a result of its accumulated technology, NIDEC can design products that satisfy customer needs in a short period of time, and manufacture them in a location close to its customers with a short delivery time. On the other hand, NIDEC tries to sell to as many customers as possible in the same application market to avoid small-lot production runs, and makes each production plant responsible for its own profitability to enhance cost-consciousness. Furthermore, NIDEC actively invests to increase production capacity ahead of anticipated growth in market demand so that it can contribute to the stimulation of business expansion, and in turn, its sales force proactively develops proposals and presents them to prospective customers willing to think out of the box. (Please refer to the attached "Activity System Map" for a more detailed account of relationship between these activities.)
Innovations that Enabled Strategy
- Through a technological innovation in the motor, NIDEC changed the HDD drive mechanism from a belt-drive to a direct-drive method. It has also reduced heat generation in HDDs and succeeded in greatly accelerating the rotation speed, which increased the recording density, and in turn miniaturized the size of HDDs to be housed in a much smaller space.
- NIDEC was the first in the industry to succeed in the mass production of FDB motors. As a result of this technology, it greatly improved the motor performance including its the high-speed rotation precision, low energy consumption, and long durability. Furthermore, the new model of fluid dynamic bearing motors, called RM type motors, are produced through an integrated manufacturing process, and enable drastically shortened manufacturing times and reduced manufacturing costs. At the same time, NIDEC internalized the manufacturing processes and improved profitability.
- NIDEC introduced a stock option program in 1996, at a time when very few companies in Japan were offering such a reward system.
- NIDEC started hiring mid-career recruits from large corporations, which was not a practice in the parts manufacturing industry in Japan at the time.
Consistency of Strategy Over Time
Since its establishment in 1973, NIDEC had practiced a strategy of specializing in brushless DC motors, identified new needs regardless of the customer industry, and attempted to win the top market share in each application market. Its original objective in starting the venture was to develop the market for brushless DC motors, but due to the high price and small size of the market for the brushless DC motors, it started out manufacturing AC motors. However, its second year of operation, one of the customers who was also working on the development of brushless DC motors went bankrupt, and NIDEC hired the technical engineers from that company. Since that time, NIDEC shifted its core business and nurtured the brushless DC motor business by replacing the standard AC motors. For example, in 1980, the early days of HDD development, while other companies developed HDDs with AC motors, NIDEC succeeded in mass-producing HDDs equipped with brushless DC motors. In 1982, it also succeeded in mass-producing brushless DC fan motors, thereby replaced AC motors with a higher performance, higher value-added alternative.
NIDEC's marketing and sales policy of seeking new applications regardless of customer industry derived from its experience in pioneering and developing the U.S. market from scratch. In Japan, the newly established NIDEC had faced strong resistance in selling to major Japanese corporations, which selected their suppliers on the basis of company size and demonstrated history as a supplier. This sales policy, developed in these early days, continues to be a viable strategy.
NIDEC's marketing and sales policy of seeking new applications regardless of customer industry derived from its experience in pioneering and developing the U.S. market from scratch. In Japan, the newly established NIDEC had faced strong resistance in selling to major Japanese corporations, which selected their suppliers on the basis of company size and demonstrated history as a supplier. This sales policy, developed in these early days, continues to be a viable strategy.
Trade-offs
- Chose to produce only brushless DC motors.
- Chose not to vertically integrate. (Thereby avoiding competition with products its customers produce.)
- Does not manufacture or sell products in small lots. (However, there is an exception. NIDEC will fill a small order to replace a brush motor, but they are sold through its subsidiary, NIDEC Copal, which has a history and experience in selling products in small lots.)
- Does not concentrate manufacturing facilities geographically. (As it produces close to customers, its production facilities consequently are dispersed around the globe.)
- Does not have exclusive supplier contracts for fear that it may become dependent on its customers as a sub-contractor.
- Does not solicit sales/orders from minor companies (because as minor customers, they are unlikely to warrant sufficient scale in production).
- Does not sell its products through trading companies. (NIDEC manufactures the products and sell them on its own. The only exception is some models of the general-purpose fan motors.)
- Will not let heirs of NIDEC founder Shigenobu Nagamori succeed the company.
- Does not put priority on short-term profitability over investment for growth.
- Does not put priority on improving profitability over expanding the brushless DC motor market.
Profitability
Both NIDEC's return on invested capital and return on sales are consistently higher than the industry average. Especially in the return on invested capital, its lead over the industry average is widening.
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on invested capital = Operating income / Average invested capital
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
Return on sales =Operating income / Net sales
Return on invested capital (ROIC) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry averag over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| 28.8%P | 19.5%P | 19.1%P | 23.9%P | 33.5%P | 40.8%P |
Return on sales (ROS) (Unit = percentage point)
| Difference from industry average over 5 year period |
Difference from industry average, by year | ||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| 7.9%P | 7.2%P | 6.6%P | 5.8%P | 4.7%P | 6.9%P |
Activity System Map
Winners PDF
- 2006 Porter Prize Winners PDF (All of the award company in this year are published. )





