Winners / Selection Rationale
Rakuten Bank, Ltd.
Rakuten Bank's value proposition is to offer customers "more convenient services and lower fees." The bank has been able to reduce costs by achieving the complete digitalization of its banking services. As a result, it is able to provide: (1) higher interest rates on deposits; and (2) home loans with low interest rates. Meanwhile, IT systems development is undertaken in-house, enabling the bank to speedily develop and launch new services. In addition, the customers can move smoothly between services, thereby improving convenience and ultimately increasing customer satisfaction.
Rakuten Bank maintains a collaborative relationship with more than 70 other Rakuten Group businesses, including Rakuten Ichiba and Rakuten Securities, Inc. The Rakuten Group forms a type of robust ecosystem. Moreover, members accrue Rakuten reward points when using any of the services offered by Rakuten-affiliated companies.
* This report was written by Professor Emi Osono of Hitsubashi University Business School, based on: (1) the materials submitted by the winner for Porter Prize screening purposes; (2) interviews conducted by the Porter Prize Organizing Committee; and (3) publicly available information. It is being published with the winner's permission.
Background of the Banking Industry and the Online Banking Industry in Japan
The banking industry collects funds through deposits, lends these funds to individuals and companies that require financing, and creates credit, thereby providing an important infrastructure for economic activities. Just consider the extent to which the global economy was affected when the banking industry put a freeze on loans in 2008 due to the global financial crisis. The impact of the banking industry is clearly visible. Taking into account the crucial role that banks play, it is no surprise that the process for opening a new bank is very involved. First, there are all kinds of preliminary screenings and inspections before a bank can get a banking license. After opening, the bank must ensure that it can secure sufficient capital. The bank must control the quality of its loan portfolio and credit administration through risk management and other methods. There are also numerous requests that must be met. These requests are either made in compliance with banking laws, or are the requirements of supervisory authorities.
Japan's banking industry had no new entrants for many years until 2000, when several online-only banks were established. Examples include Japan Net Bank, which has obtained a standard banking license. Japan Net Bank was created jointly by Sakura Bank, which is currently Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC), Fujitsu Ltd., and Nippon Life Insurance Company (Nihon Seimei). (Later, Japan Net Bank became a subsidiary of Z Financial Corporation, which is a subsidiary of Z Holdings Corporation. Japan Net Bank plans to change its name to PayPay Bank in April 2021.)
The emergence of online-only banks was prompted by the widespread adoption of the internet. An online-only bank provides a deposit account, and can make online banking transfers into that account or perform other online transactions, all at the customer's request. Because the online-only bank has obtained a banking license, it can also provide mortgage loans and other loans, as well as financing services. Unlike conventional banks, online-only banks do not need to build a network of branches or set up a dedicated ATM network. Thus, the online-only bank's costs are lower. For customers, this translates into higher interest rates on deposits, lower fee charges, and lower interest rates on loans. However, it is not the case that all online banks do not maintain branches, do not have ATMs, and do not use hard-copy documentation. This varies, depending on the customer's needs and the bank's in-house procedures. Online banks have a certain degree of freedom, and are able to design their own optimal combination of online and offline services. In the meantime, conventional banks have started opening online "branches." Although the online services are more convenient for customers, the amount such banks charge for their online services is not that much different from their normal fees. As a result, conventional banks are unable to compete with online-only banks in terms of price competitiveness.
Unique Value Proposition
Rakuten Bank is an internet bank that does not maintain branches for face-to-face consultations or its own dedicated ATM network. Rakuten Bank is Japan's largest internet bank, with total accounts of 8.68 million, as of March 31, 2020.
The bank's value proposition is to provide its internet-using customers with "more convenient services and lower fees." "More convenient services" refers not only to the banking services offered by conventional banks, but also the convenience created by combining banking services with a wide variety of financial and other services offered by Rakuten-affiliated companies.
Rakuten Bank offers the following services: Deposits (yen & foreign currencies); financing (credit card loans, mortgage loans, educational loans); bank deposit transfers, remittance services (credit cards, debit cards, prepaid cards, money transfers, etc.); the deposit and withdrawal of money (at affiliated ATMs); asset management apps (Money Support); and payments for Takurakuji and BIG lottery tickets, Toto (J-league soccer pools), and public race tracks, etc.(*1) In addition, customers can move seamlessly between Rakuten Bank and other Rakuten Group companies, including an investment trust bank, a securities company, and an insurance company, when other non-banking services are required.
Nearly all of these various services are accessible from a single smartphone app. That is to say, anyone with a smartphone can access all of these services. There is no need to start up a personal computer. Normally, among an online bank's smartphone applications there is a dedicated app for opening up a new account, and a dedicated app for showing the account balance. Even among the apps provided by a single bank, these apps are usually divided according to function. Rakuten Bank has only one app. Users can feel a degree of comfort with this app, as there is no need to move between apps.
Furthermore, Rakuten Bank's app is easy to use. The bank monitors customers' online behavior, noting page transitions, breakaway points and other types of monitoring issues, and identifies any points that might be difficult to understand, or that might be a source of stress for customers. Rakuten Bank's in-house IT systems development team has full knowledge of banking operations, and is able to quickly make changes and improvements. Many banks outsource the development, operation, and maintenance of their own IT systems. However, the fact that Rakuten Bank can build its own system in-house is unique. As background, Rakuten Bank is committed to grasping in real time customers' feedback about its banking services. It then quickly responds by making improvements. Making the IT system a built-in part of operations brings the following competitive advantages: (1) speed (with regard to systems development and improvements); (2) cost; and (3) flexibility. This high-speed improvement cycle is also applied to the bank's services. In this way, the bank is able to provide those services most desired by customers as well as swift service and competitive low fees.
Rakuten Bank's interest on deposits, rates on financing, and its service charge pricing system are all reasonable and set at a level that is advantageous to the customer. For example, when it comes to the administrative fees for financing a home loan, many banks will set a fixed rate. Rakuten Bank, however, charged a flat rate of 300,000 yen (excluding tax) on home loans in November 2020. (This amount comes to US$2,884.62, at 104 yen/US$.) Some banks will charge customers 2% of the loan amount as an administrative fee. For the customer taking out a home loan of 50 million yen (US$480,769.23), that individual would be required to pay an administrative fee of 1,000,000 yen (US$9,615.38). Rakuten Bank charges 300,000 yen (US$2,884.62). This is a major reason why customers would choose Rakuten Bank over other banks. Logically, the administrative costs are supposed to be the same regardless of the amount borrowed. The bank has heard customers often ask: "Why is it that we have to pay a higher administrative fee when we take out a larger mortgage loan?" By committing to a more reasonable fee structure, Rakuten Bank has adopted a stance that is more acceptable to customers.
In addition, Rakuten Bank offers customers a rewards program named the "Happy Program." If you already possess a Rakuten ID, it is possible to use that same ID when opening a Rakuten Bank account. The customer's "stage" is determined based on usage (number of transactions and total assets). Customers in a "high stage" are allocated a larger number of Rakuten points. Points earned through the Happy Program can be used as payment for the bank transfer fees charged by Rakuten Bank. These points can also be used for services provided by other Rakuten Group companies. In addition, many net retailers and brick-and-mortar stores will accept Rakuten points as payment. Rakuten points received through a rewards program are used more frequently than any other point system in Japan, and there are many point systems currently in use. Consequently, it is the largest-scale rewards program in Japan's banking industry. For customers, the usability of these points represents significant value. This is one of Rakuten Bank's strengths that other banks cannot imitate. The Happy Program raises the effectiveness of Rakuten Bank's marketing efforts, and is an important element that plays a key role in fostering a high degree of loyalty among customers.
Rakuten Bank's cost advantage is what makes possible its competitive interest rates, fees and commissions that are advantageous to the customer, and its robust rewards program. In addition, the bank is able to minimize its new customer acquisition cost. Like Rakuten Bank, the "Rakuten Ichiba" marketplace (a large internet shopping mall) is a member of the Rakuten Group. There are about 30 million members who make purchases with a high rate of frequency. Also, over 20 million members have a Rakuten credit card, and they use their Rakuten credit card monthly. Rakuten Bank has been able to access the strong customer base of all the other companies under the Rakuten Group's umbrella. Rakuten Bank has succeeded largely thanks to this convenient access to new customers. Furthermore, the bank promotes all types of banking services to its existing customers, as well as services offered by other Group members, in a type of "cross-selling." In this way, the bank is able to minimize its new customer acquisition costs. Meanwhile, system development costs are kept at a minimum by making IT systems development an in-house function. Compared with banks that operate branches and have their own bank ATM machines, the online-only Rakuten Bank has been able to enjoy substantial cost savings. This is a major point that sets the bank apart from its competitors.
For its corporate customers, Rakuten Bank maintains a sales team. An in-house sales team is quite unusual among internet-based banks. The members of this sales team make face-to-face sales calls. Rakuten Bank's sales staff will visit the corporate customer's office or factory, and speak directly with the executives. The bank's sales staff inquire about the issues facing management, and then provide a tailor-made service that utilizes IT technology, which is Rakuten Bank's strength. An in-house team of knowledgeable IT systems developers makes it possible to provide these services in a speedy manner.
(*1) Rakuten Bank's website, https://www.rakuten-bank.co.jp/, accessed on Nov. 25, 2020.
Unique Value Chain
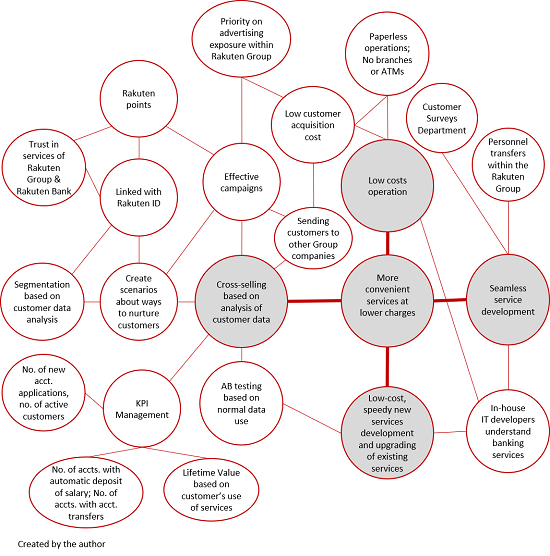
Rakuten Bank's value chain is designed to enable the bank to develop superior banking services, offer them at a lower fee, and seamlessly provide a wide variety of services, taking full advantage of synergies with other Rakuten Group companies. The most prominent features are: (1) service development; (2) new customer acquisition; (3) cross-selling; (4) IT systems development; and (5) human resource management.
◆ Development of servicesAt Rakuten Bank, a subcommittee has been set up to discuss the bank's new services and consider ways to upgrade existing services. All employees are welcome to participate. Topics of discussion include: (1) the customer needs that would be met by making improvements to existing services or developing new services; (2) the development processes and the costs involved in developing IT systems for new services and the upgrading of existing services; (3) the challenges associated with such improvements and development projects; and (4) marketing activities that would enable the bank to recoup investments made for the development of new services and the upgrading of existing services. All employees are required to participate in discussions that go beyond the scope of their own departments. This experience gives bank employees the opportunity to gain a better understanding of the customers' needs and deepens their knowledge about systems development, while helping them to increase their marketing know-how.
◆ New customer acquisitionThe Rakuten Group possesses internet marketing-related know-how that is based on data. Rakuten Bank makes full use of this know-how. Consequently, Rakuten Bank can efficiently reach prospective new customers by leveraging the services of Group companies. For example, Rakuten Bank puts a higher priority on increasing its exposure within the Rakuten Group, as this is a more effective and low-cost way to attract new customers than placing advertisements outside of the Group. External advertising is positioned as a supplementary option. This approach makes it possible to control advertising costs and keep them low. This cost-savings makes it possible for Rakuten Bank to upgrade the rewards (Rakuten points) given to customers opening new accounts, which makes the bank even more appealing to customers.
◆ Cross-selling of the bank's servicesWith regard to Rakuten Bank's practice of cross-selling banking services to customers, the customer data in the bank's possession (including the customer's attributes, service usage history, and history of online transactions), is divided into segments, taking into account each customer's preferences (gleaned from all types of customer data held by other Rakuten Group companies). Rakuten Bank then designs products and services that would appeal to each of these various segments. Next, the bank develops a sales campaign that will have maximum appeal for the specific segment in question. Finally, the bank implements this campaign. This same process is undertaken for each customer segment.
Based on the customer data, it is sometimes possible to discover the customers' latent, unmet needs for some products or services. The bank creates a story that will help customers to understand the value of these products or services. The newly created stories are then featured in sales campaigns. By raising awareness in this way, customers develop an understanding about the bank's peripheral services. Ultimately, this approach motivates customers to seek out those products and services.
With regard to all of the bank's campaigns, Rakuten points can be used. This feature increases the customer appeal of the bank's promotional campaigns. The end result is that Rakuten Bank has a high degree of success with cross-selling as a marketing tool.
◆ Referring bank customers to other Group companies and cross-sellingTo its new customers Rakuten Bank proposes a selection of the Group's new services, taking into account each customer's preferences. On such occasion, the bank's data and the Group's data are utilized. The ability to send customers to other companies reflects: (1) the customers' trust in Rakuten Bank; and (2) the positive impact of various campaigns in which Rakuten points can be used.
◆ KPI managementRakuten Bank's key performance indicators (KPIs) include the following: (1) the number of daily new account applications; (2) the number of active customers; (3) total customer lifetime value (CLV) for Rakuten Bank, which is the result of lifetime value per customer (based on the individual customer's service usage history) multiplied by the number of active customers; (4) the number of direct payroll deposit accounts and the number of account-to-account transfers (as representative indicators of customer activation). Taking these key performance indicators into account, the bank revises its marketing plans and reviews its strategies. For example, the new customer acquisition cost is controlled by taking into consideration the customer lifetime value (CLV).
◆ IT systems developmentRakuten Bank's IT systems have been developed in-house by employees who are knowledgeable about banking operations. This team is responsible for undertaking systems development, systems operation, and maintenance. Moreover, the members of this team continuously undertake service improvements, such as user interface (UI) and user experience (UX), in a precise and speedy manner. In addition, in-house development of IT systems offers advantages with regard to the development of new services. For example, it becomes possible to design services that precisely meet customer needs and to create new high-quality services in a very short time.
◆ Human Resource ManagementRakuten Bank's policy regarding the training of personnel is to place high value on expertise. At the same time, the bank aims to foster a workforce of employees who have a breadth of knowledge and experience on top of that expertise. Individual employees should be able to combine banking services with other services from a variety of fields. In particular, personnel transfers are assigned taking into account the development of the individual's potential. New work assignments provide an opportunity for new information and learning experiences, especially considering that companies within the Rakuten Group take part in these personnel exchanges. This practice makes it possible for people with areas of expertise and work experience outside of banking to bring their thinking into the bank as an organization. This facilitates the creation of an environment that allows for a diversity of opinions and perspectives among the bank's employees. Thus, employees do not have the kind of narrow perspective that a limited knowledge of anything beyond banking services would produce. The bank's employees are expected to become able to take into consideration the customer's life as a whole in the designing of banking services.
Interaction between the bank's personnel and those of Rakuten Group companies also helps the providers of other services deepen their understanding about the bank's services. The ability to offer banking services in combination with other services makes it possible for Rakuten Bank to further enhance customer convenience. Moreover, the ability to accrue Rakuten points has the effect of reducing the actual cost of banking services for users and reinforces their sense that they are getting a bargain.
The bank's employees must work in the bank's call center at least once a month, after undergoing training. This gives employees the chance to speak directly with customers. The bank believes that in order to gain the customers' trust, its services have to be improved on an ongoing basis and in a speedy manner. The bank considers that the first step is to precisely understand the customers' needs, and then identify any changing needs. It is for this reason that all employees are given the chance to speak directly with customers and that the organization as a whole makes it a priority to improve both the quality of its banking services and the speed with which those services are upgraded.
Fit Among Activities
The following are the four main strategic themes at Rakuten Bank: (1) Swiftly expanding Rakuten Bank's customer base by leveraging the Rakuten Group's customer base to accurately identify prospective new customers and offer them a variety of customized services that precisely meet their needs. (2) Making continuous efforts to improve customer services and increase the service lineup by launching new services in a short time and at a low cost (both advantages afforded by the use of proprietary IT systems). (3) Cross-selling by utilizing both the bank's data and the Rakuten Group's data, and through the promotion of Group companies' services to the bank's customers. (4) Strengthening the customers' trust in the bank's services and the services of Group companies.
Finally, the pursuit of the following core activities that mutually reinforce all the bank's other activities: Cross-selling, based on an analysis of customer data; the development of seamless services; and continuous and speedy improvements in IT systems development that will further enhance the bank's reliability. (Please refer to Rakuten Bank, Limited's activity system map, which appears at the end of this report.)
Innovation that Enabled Strategy
- A money transfer service that does not require the payee's account number. The Bank's Kantan Furikomi or Easy Deposit settlement service enables customers to send money using Merumane (Mail Money), Facebook Pay, or Viber's money transfer service. With Merumane (Mail Money) all that is needed is an email address and the payee's full name.
- Free-of-charge asset management tool "Money Support," which is available to all account holders.
- Rakuten Bank's convenience store payment service. By using the Rakuten Bank app to read the barcode on the convenience store payment service's transfer slip, the customer can make a direct payment without having to make a trip to the store. Usage of this electronic settlement service accrues Rakuten points.
- Rakuten Bank debit card pays the highest level of reward points in the industry. Without any conditions, 1% of the debit card's user charge is returned to customers as Rakuten reward points.
- Rakuten Bank app and website. Customers can log into the Rakuten Bank app without a login password by using fingerprint authentication. In the case of the social media network payment service "Viber," the Rakuten Bank app and the Viber app are connected by a deep link. Thus, it is possible to move seamlessly to the Rakuten Bank app's "Viber Money Transfer" option from the Viber chat site, enabling money transfers to be conducted smoothly.
Trade-offs
- Rakuten Bank has decided to forego paper-based services, in principle. (This excludes the mortgage loan business, as the current industry practice is to require hard-copy documentation.)
- The company does not maintain a network of real branches, and does not provide face-to-face services, in principle. That said, the exception is mortgage loans (the most expensive purchase individuals will make during their lifetime). Such customers seek reassurance in face-to-face consultations. Thus, the bank offers its mortgage loan customers the option of a web meeting.
- Does not have its own dedicated ATM network. However, customers need to make withdrawals from their accounts. The knowledge that they can make withdrawals anytime brings customers a sense of security, and makes it possible to expand cashless payments. For this reason, Rakuten Bank has formed alliance agreements with other ATM operators, enabling customers to use the ATM networks of megabanks, convenience stores, and Japan Post Bank. The bank's customers have access to more than 90,000 ATMs nationwide.
- Does not hold government bonds as investment vehicles.
- Does not undertake over-the-counter sales of investment trusts. Over-the-counter sales of investment trusts are a major source of revenue for many banks. The priority of such banks is to provide a broad lineup of products that will satisfy the customers' diverse needs. These banks must continually invest in their investment trust systems. Rakuten Bank merely refers interested customers to the Rakuten Group affiliate Rakuten Securities, which provides customers with investment trust services and also arranges for stock purchases.
Consistency of Strategy over Time
Rakuten Bank's predecessor was eBank Bank, which was established in 2000. It began operating as Japan's third internet bank in July 2001. The bank then formed a capital and business tie-up with Rakuten, Inc. in August 2008. The bank changed its trade name to Rakuten Bank in 2010. With this name change, Rakuten aimed to make clear the bank's positioning as a member of the Rakuten Group and emphasize the superior customer convenience that the bank can provide by taking advantage of synergies with other Rakuten Group companies. (*2)
Thus, Rakuten Bank's first basic strategy is to grow its business through new customer acquisition, specifically by leveraging the customer base of other Rakuten Group companies. (Membership for all Rakuten Group companies combined totaled about 100 million people.) The second basic strategy is to create better services through: (1) the cross-selling of the Group's other businesses and services; and (2) the creation of customized services by combining banking services with other services offered by Group members. The bank has consistently pursued these strategies from the very beginning.
As a first step, the Rakuten Group made efforts groupwide to identify latent demand among existing customers. Efforts were made to leverage all services, and reach prospective customers without spending much time or money. The bank was also able to very efficiently acquire new customers from among the existing customers of other Rakuten Group companies. The bank has remained committed to offering convenient services at a reasonable price, while consistently pursuing the cross-selling of various products and services.
Next, the bank has made its banking services more attractive by offering them in combination with the services of other Group companies. Rakuten Bank has continued to follow these same strategies for acquiring new customers. In April 2011, Rakuten Bank launched its "Money Bridge" service, a banking account linked with an account at Rakuten Securities. Another success story was Rakuten Bank's participation in the SPU program (Rakuten Ichiba's Super Point Up Program) in July 2018. Since its participation in the SPU program, the bank's acquisition of new customers has risen dramatically. Moreover, all of the financial companies in the Rakuten Group have formed tie-ups as agency service providers for the bank: Rakuten Securities, Inc. and Rakuten Life Insurance Co., Ltd. in 2016; Rakuten General Insurance Co., Ltd. and Rakuten Card Co., Ltd. in 2019. This arrangement has allowed the financial companies to undertake promotion and registration for the opening of an ordinary deposit account on behalf of Rakuten Bank. (*3) It was designed to improve customer convenience and increase new customer acquisition.
Meanwhile, Rakuten Bank has introduced its customers to other Group companies. This approach is based on the thinking that bank customers who use more services offered by Group companies will feel greater loyalty toward the Rakuten Group. In July 2010, Rakuten Bank started serving as an agent for the financial products of Rakuten Securities. The bank also signed an agency agreement with Rakuten Life Insurance in March 2013, and Rakuten General Insurance in April 2019. As an example of a tie-up with the service of a non-financial Group member, there is Viber's money transfer system, which uses the Group's Viber messaging app. This has made Rakuten Group services more easily accessible to Rakuten Bank's customers, and has strengthened customer loyalty toward the Rakuten Group. As a result, it has become easier for Rakuten Bank to cross-sell its products and services.
The bank takes a different approach when dealing with its corporate customers. Rakuten Bank makes direct sales calls, speaking face-to-face with the management. During the meeting, the sales staff member makes an effort to accurately identify the customer's needs, and then offers a selection of customized products and services, utilizing a cross-selling approach.
(*2) Rakuten, Inc.'s news release, "Notification that Rakuten has changed the name of its subsidiary (eBank Bank), Jan. 21, 2010, https://corp.rakuten.co.jp/news/press/2010/0121_01.html, accessed on Nov. 25, 2020.
(*3) Rakuten Life Insurance Co., Ltd.'s website, https://www.rakuten-sonpo.co.jp/contact/tabid/1087/Default.aspx, accessed on Nov. 25, 2020.
Profitability
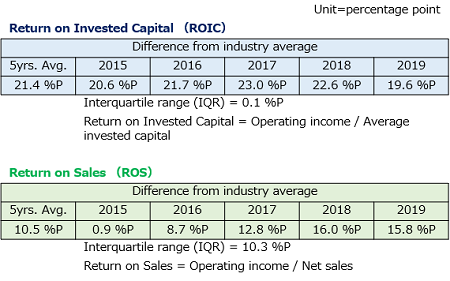
Rakuten Bank, Ltd. saw its five-year averages for return on invested capital (ROIC) and the return on sales (ROS) widely exceed the industry average. (Profitability analysis was conducted by PwC Japan.)
Activity System Map of Rakuten Bank
Winners PDF
- 2020 Winners Pdf (All of the award company in this year are published. )






